Background: The currently available, clinically approved factor XIII (fXIII) activity assays rely on indirect measurement of activated fXIII transglutaminase activity by detecting "ammonia-release" during an intermediate step of the reaction. Unfortunately, this assay is also sensitive to fXIII-independent ammonia-producing reactions that may take place physiologically in plasma, rendering it prone to overestimate fXIII activity, especially when levels are <10% (0.1 IU/mL). High quality quantitative fXIII activity assays are required for the accurate and timely diagnosis of fXIII deficiency. fXIII circulates in complex with fibrinogen, and activated fXIII retards fibrinolysis by incorporating α2-antiplasmin (α2AP), a potent antifibrinolytic, into the forming clot via intermolecular α2AP:fibrin crosslinks. We have thus developed a new fXIII transglutaminase activity assay that directly measures α2-AP incorporation onto captured fibrin(ogen):fXIII complexes. We hypothesized that this novel assay has high sensitivity in detecting FXIII activity, especially at the low end of the dynamic range (<10%; <0.01 IU/mL).
Methods: A standard curve was established by diluting known concentrations of recombinant factor XIII-A (rFXIII-A; Tretten) into (1) fXIII-A congenitally deficient and (2) fXIII immunodepleted plasma to determine if our assay is able to detect variable fXIII concentrations from 1 to 200% (0.01 - 2 IU/mL).
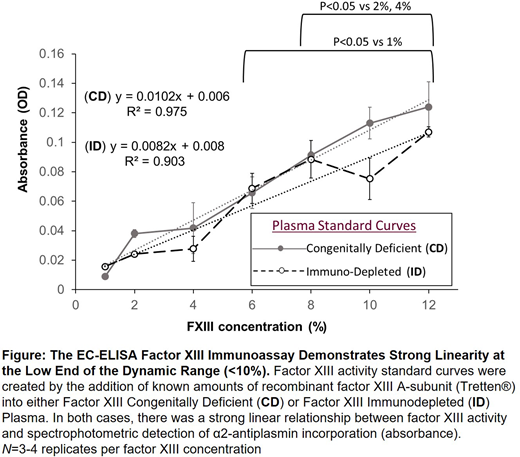
Results: We demonstrated that α2-AP incorporation is dependent upon rfXIII-A concentration in the starting sample and was linear from 1-12% (0.01 - 0.12 IU/mL; Figure). Further expansion of the standard curve to include all concentrations within the normal physiologic range demonstrated that the assay remains strongly linear from 1-20% (0.01 - 0.2 IU/mL; R2 0.966). Moderate linearity (R2 0.908) extended to 50% (0.5 IU/mL). The curve plateaued between 50%-200% (0.5 IU/mL- 2 IU/mL). Thus, the dynamic range of the Enzyme Capture-ELISA is expected within 1-50% (0.01 - 0.5 IU/mL).
Conclusion: We conclude that Enzyme Capture-ELISA is a promising novel method for accurate detection of FXIII activity and is expected to improve sensitivity at low levels (<20%; <0.02 IU/mL), which are most clinically relevant. Further experiments are needed to refine the upper limit of assay linearity and thereby refine the dynamic range of the assay. With further optimization and validation, the EC-ELISA method may provide an improved diagnostic assay.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal